Differences Between PFM and Zirconia Crowns
2025-03-12
In dental restoration, the choice of crown material is crucial, the current market process of crown material is divided into several kinds, such as metal crowns, glass ceramic crowns,
PFM (porcelain fused to metal crowns), zirconia crowns, PFM (porcelain fused to metal crowns) had a long time to dominate the mainstream, and in recent years, zirconia crowns due to its good aesthetic properties and biocompatibility quickly rise.
This article mainly introduces the differences between PFM crowns and zirconia crowns for your reference.
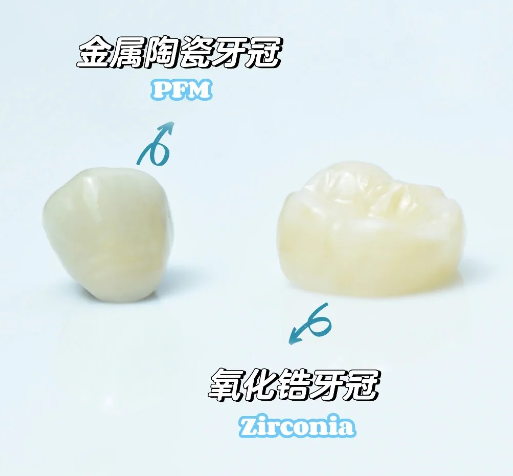
PFM (Porcelain Fused to Metal Crowns)
Structurally, it consists of an internal metal base (e.g. cobalt chromium alloy or precious metal) + an external porcelain layer, which is a composite material. This material has been in use for decades,
and after many iterations and improvements, it now has a lot of audience groups, and the technology is more mature, and it is mainly used for restoration of anterior and posterior teeth, and has a better aesthetic appearance.
Zirconia crowns
Zirconia crowns, the main component of which is zirconia powder, are an all-ceramic material with excellent biocompatibility and aesthetic properties, and are easy to process.
Thanks to the development of CAD/CAM technology this year and the entry of Chinese zirconium oxide manufacturers, the price of zirconium oxide denture has been slightly reduced,
and zirconium oxide crowns are now one of the mainstream materials.
Zirconia denture is mainly used for single crowns, bridges, inlays and veneers.
3. PFM vs. zirconia crowns: comparison of core differences
Comparison factors PFM crowns Zirconia crowns
| Comparison Factors | PFM Crowns | Zirconia Crowns |
|---|
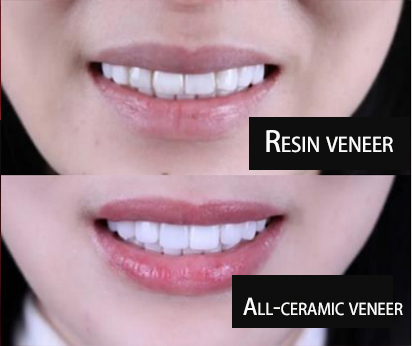
| Aesthetics | The porcelain layer can mimic tooth color, but over time, chipping or metal edge exposure may occur. | Natural color with excellent translucency, closely resembling real teeth, without metal shadows. |
| Strength & Durability | The metal substructure provides good strength, making it suitable for posterior teeth and long span bridges. | High-strength zirconia (>1000 MPa) withstands occlusal forces but may develop cracks under extreme conditions. |
| Biocompatibility | The metal component may cause allergic reactions or gum discoloration in some patients. | Highly biocompatible, allergy-free, and gum-friendly. |
| Manufacturing Process | Requires multiple layers of porcelain application and high-temperature sintering, making the process more complex. | Designed using CAD/CAM technology and CNC milling, ensuring higher precision. |
| Long-term Stability | The porcelain layer may chip over time, and metal components may oxidize. | Zirconia is corrosion-resistant, less prone to chipping, and more durable. |
| Cost | Moderately priced, but PFM crowns with precious metals can be expensive. | Relatively higher cost, but offers excellent value and long-term cost-effectiveness. |
4. Crowd analysis: which crown is better for you?
Patients who are suitable for PFM
1. Relatively low budget, needing an affordable and durable restorative solution.
2. Low aesthetic performance requirements, the main consideration is practicality, do not mind the possible aesthetic impact of metal substrate.
Suitable for patients who choose zirconia crowns
1. Patients who require higher aesthetic performance, especially for anterior restorations.
2. Patients who are allergic to metal and require high biocompatibility.
3. Want zirconia crowns to bring longer lasting use.
4. Relatively good budget and can wait for a long time.
5. Conclusion: How to make the best choice?
There is no absolutely correct choice, only a relatively satisfactory solution. Choosing a specific crown material also requires a combination of the
dentist's communication of the patient's oral condition, budget, time, aesthetics, and other aspects to give the right advice.
Summary:
PFM crowns and zirconia crowns each have their advantages and suitable scenarios. The choice of restoration depends on the patient's specific needs, dental condition, and the dentist's advice.
honchon smile is a professional dental zirconia block manufacturer and supplier. We provide high-quality dental zirconia blocks, multilayer zirconia blocks, pre-colored dental zirconia blocks. Welcome to discuss cooperation with us!