Performance Requirements of Wax-based Materials in Dentistry
2024-04-07
Performance Requirements of Wax-based Materials in Dentistry
 What are wax block materials? The wax used in the dental clinical fabrication process is called wax material, which is used for the fabrication of restorative waxes, wax bases, wax dikes, wax brackets and temporary fixation. The quality of the wax material is related to the quality of the fabricated restorations, so the clinical requirements for the wax material are high.
What are wax block materials? The wax used in the dental clinical fabrication process is called wax material, which is used for the fabrication of restorative waxes, wax bases, wax dikes, wax brackets and temporary fixation. The quality of the wax material is related to the quality of the fabricated restorations, so the clinical requirements for the wax material are high.
Classification of wax-based materials
There are animal waxes (beeswax, worm wax, Chuan wax, whale wax), vegetable waxes (carnauba wax, capital wax, coconut wax, etc.), mineral waxes (paraffin wax, ground wax, etc.), and synthetic waxes (plastic waxes) according to the nature of the wax.
According to the classification of wax usage, there are impression wax, model wax and shaping wax.
Properties of wax-shaped materials
1, Melting and softening temperature
The melting point range of paraffin wax is 42~62℃, and that of carnauba wax is 84~90℃. First, the wax itself has a specific softening point temperature, one refers to the temperature available for operation and shaping in a broad sense. In places where the temperature changes greatly during the four seasons, people should pay special attention to the conditions of use of wax and use it according to the instructions.
2. Thermal expansion rate
The thermal expansion rate of wax for dental use should be small. The general wax with low thermal conductivity and high thermal expansion rate, and the wax with high thermal expansion rate also has high shrinkage rate. Choosing wax with low thermal expansion rate can reduce its shrinkage rate and improve the accuracy of the wax mold.
3.Fluidity
The fluidity of wax refers to the combination of rheology and plasticity. The pressurized shortening rate is an important observation indicator of rheology, which is strictly regulated internationally, especially for inlay waxes with strict technical parameters. The fluidity of the wax affects the accuracy of the wax pattern. The size of wax fluidity is determined by the density, viscosity and softening temperature of the wax itself.
4. Other properties
1) The color of the wax, to be clearly distinguished from the oral cavity-related tissue, and the color of the model material. Mostly blue or green to facilitate accurate operation.
2) Casting wax can be vaporized during high temperature casting and does not leave cauterized residue after evaporation.
3) The base tray wax can be removed when boxing and de-waxing, leaving no residue.
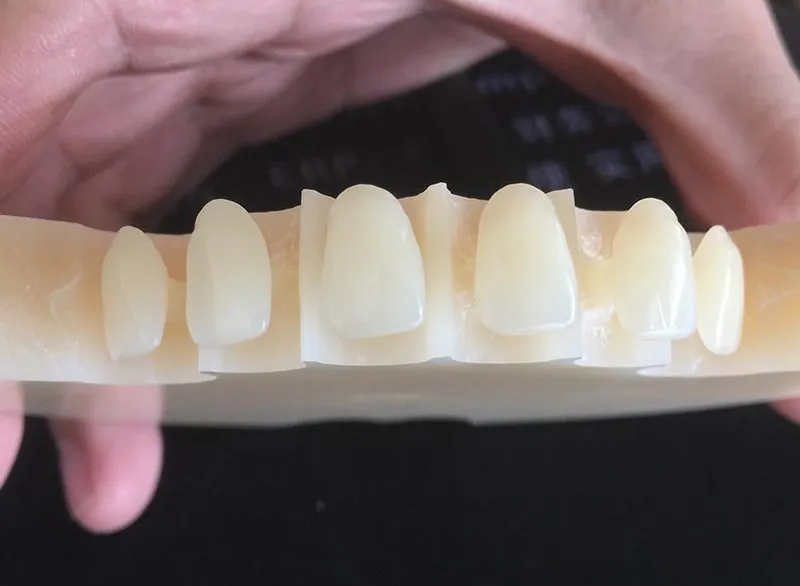
Casting wax
Casting wax consists of 60% paraffin wax, 25% carnauba wax, 10% ground wax and 5% beeswax.
Paraffin wax has good fluidity and has certain shrinkage after cooling and solidifying. It has low hardness, brittle, easy to break, and poor sculptability. Ground wax has good toughness and high luster. Beeswax is soft, easy to bend, toughness, plasticity, good carving, and luster. Carnauba wax has strong luster, high hardness and high brittleness.
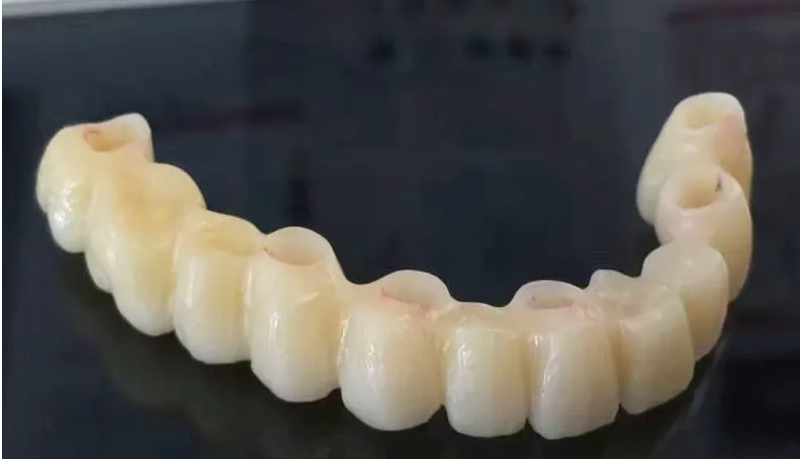
Casting wax is mainly used for making wax molds of various metal casting restorations. High precision and good strength ensure that the wax mold is not deformed when it is taken out.
Dental wax is widely used in dental CAD. HONCHON SMILE wax blocks have a low coefficient of expansion, are environmentally friendly, non-cracking and easy to grind. It can be used with common molten materials in the market to improve the casting success rate.
As we are a direct manufacturer of dental wax blocks for more than 10 years, our dental waxes are of very high quality and in order to give more benefits to our customers, we have only cost price, if you are interested please contact us as soon as possible to get the details.